The Guidelines for the standardisation of pavement structures of traffic areas (RStO) contain example cross-sections and definitions of associated terms
Search
Company locations
The whole picture – with just a single click. Find out here where our branches are located, what services they offer and how to contact them.
REMONDIS Group locations
Discover the world of REMONDIS with its approx. 900 branches and associated companies in over 30 countries across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia.
Technologically sound: incinerator bottom ash (IBA)
Roads and earthworks are subject to clear construction specifications. The definition of national technical regulations for road and transport systems are the responsibility of the various committees of the German Road and Transportation Research Association (Forschungsgesellschaft für Straßen- und Verkehrswesen, short FGSV). The regulations cover the areas of traffic planning, traffic management, traffic engineering, road design, road construction, road operation and road maintenance. The publications of the FGSV are generally endorsed by the German federal states. However, they can make changes so that requirements in federal states can differ slightly.
IBA is part of the official technical framework
With regard to the requirements for incinerator bottom ash in road construction and earthworks, numerous publications must be observed. In addition to the R-guidelines, the Technical delivery terms (TL), Additional technical conditions (ZTV) and Technical testing regulations (TP), which apply to all aggregates, special Technical bulletins regarding the material must also be observed.
| R1 regulations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Technical delivery terms | Additional technical conditions of contract | Technical testing regulations |
| TL Gestein-StB 04/23 | TP Gestein-StB | |
| TL Pflaster-StB 06/15 | ZTV Pflaster-StB 20 | |
| TL SoB-StB 20 | ZTV SoB-StB 20 | |
| TL G SoB-StB 20/23 | ||
| TL BuB E-StB 20/23 | ZTV E-StB 17 | |
| TL Asphalt-StB 07/13 | ZTV Asphalt-StB 07/13 | TP Asphalt-StB |
| TL Beton-StB 07 | ZTV Beton-StB 07 | TP Beton-StB |
| Technical bulletins | ||
| Richtlinien für die Standardisierung des Oberbaus von Verkehrsflächen (RStO) | ||
| Richtlinien für umweltverträgliche Anwendung von mineralischen Ersatzbaustoffen im Straßenbau (RuA-StB 23) | ||
| Richtlinien für die umweltverträgliche Verwertung von Ausbaustoffen mit teer-/pechtypischen Bestandteilen sowie für die Verwertung von Ausbauasphalt im Straßenbau (RuVA-StB 01) | ||
| R2 regulations |
|---|
| Guidelines |
| Merkblatt über die Wiederverwertung von mineralischen Baustoffen als Recyclingbaustoffe im Straßenbau (M RC) |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Hausmüllverbrennungsasche im Straßenbau (M HMVA) |
| Merkblatt über Bauweisen für Technische Sicherungsmaßnahmen beim Einsatz von Böden und Baustoffen mit umweltrelevanten Inhaltsstoffen im Erdbau (M TS E) |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Kraftwerksnebenprodukten im Straßenbau (M KNP) |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Gießereireststoffen im Straßenbau |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Metallhüttenschlacken im Straßenbau (M MHS) |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Hüttenmineralstoffgemischen im Straßenbau (M HMGM) |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Eisenhüttenschlacken im Straßenbau (M EHS) |
| Merkblatt über Bodenbehandlungen mit Bindemitteln (M BmB) |
| Merkblatt für die Verdichtung des Untergrundes und Unterbaues im Straßenbau |
| Merkblatt zur Wiederverwendung von Beton aus Fahrbahndecken |
| Merkblatt über die Verwendung von Boden ohne und mit Fremdbestandteilen im Straßenbau (M BomF) |
| Merkblatt für die Wiederverwendung von Asphalt (M WA) |
Secondary aggregates in road construction: relevant regulations of the German Road and Transportation Research Association (FGSV)
Road design principles
Regarding the road structure, the Guidelines for the standardisation of pavement structures of traffic areas (Richtlinien für die Standardisierung des Oberbaus von Verkehrsflächen, short RStO) must be observed. The following illustration depicts a simplified road cross section. A distinction is made between the naturally existing subsoil, the subgrade and subbase and the pavement structure. The latter consists of two to three base layers, but usually at least a frost blanket layer and a base course.
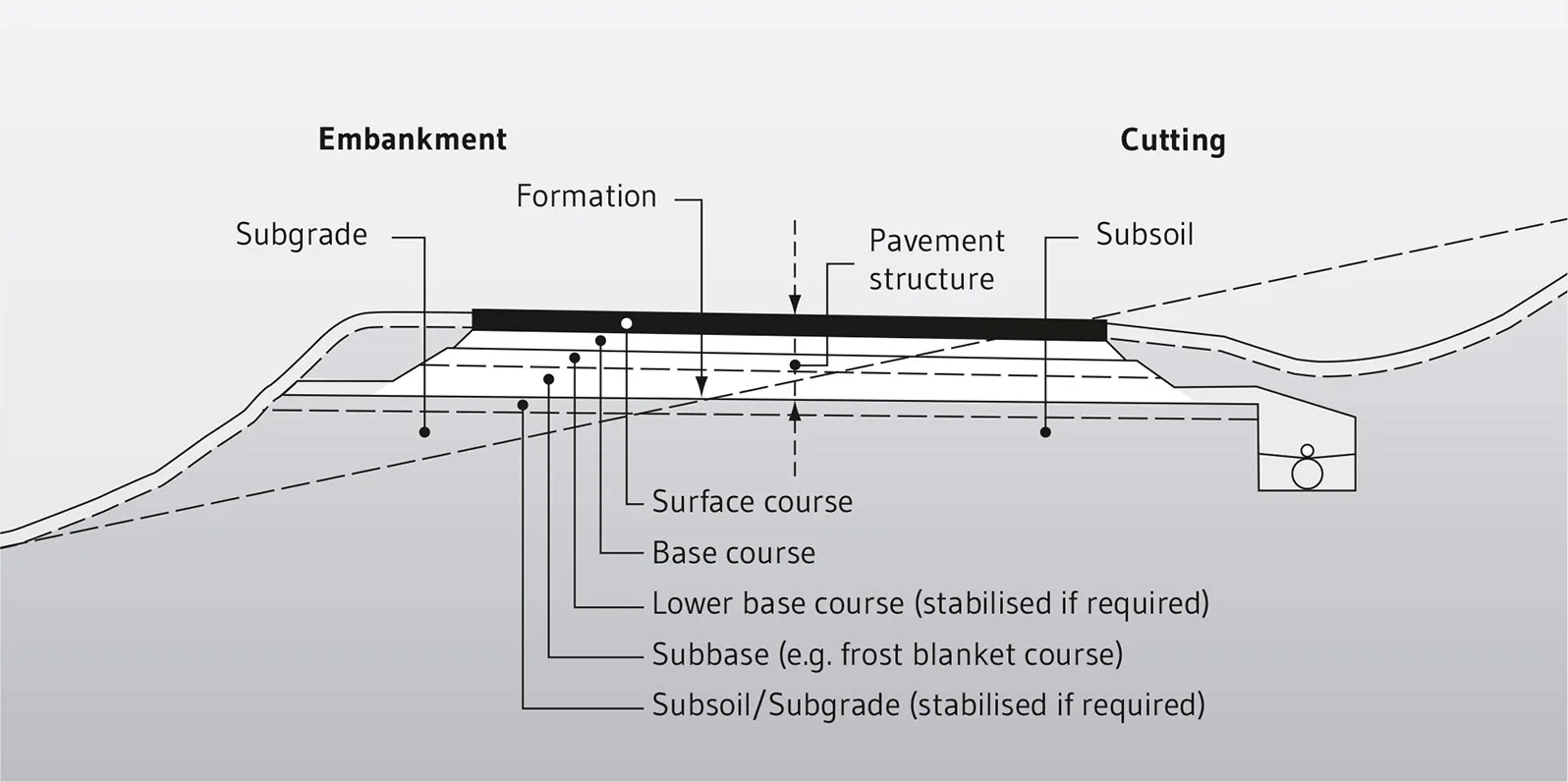
Assignment of load classes based on road type
The FGSV regulations distinguish construction classes. Each road is assigned to one of these construction classes depending on the traffic load. A distinction is made between classes with decreasing traffic load, starting with Bk100 (highest load, such as motorways or rural roads), followed by classes Bk10 to Bk0.3, with Bk0.3 for the lowest traffic volume, e.g. for a residential road. The load class affects, among other things, the type of construction and the structure of the road surface.
| Typical design situation | Load class according to RStO 12 |
|---|---|
| Open road (high-speed roads) | Bk10 to Bk100 |
| Link road | Bk3.2/Bk10 |
| Industrial site access road | Bk3.2 to Bk100 |
| Business access road | Bk1.8 to Bk100 |
| Main shopping street | Bk1.8 to Bk10 |
| Collector street | Bk1.0 to Bk3.2 |
| Residential street | Bk0.3/Bk1.0 |
| Residential pathway | Bk0.3 |
Load classes for typical design situations
Structural suitability of IBA
From a structural point of view, incinerator bottom ash can be used as a substitute building material in the following road applications:
- subgrade
- hydraulic soil improvement, soil consolidation
- dam, embankment, backfill
- frost blanket course in load classes Bk0,3 to Bk3,2
- base and subbase courses for roads subject to low traffic as well as cycle paths and footpaths
The environmental specifications for the use of incinerator bottom ash must be observed additionally.
Handbook on secondary aggregates
Find out more about this topic with details on structural and ecological backgrounds in our latest edition of the German Handbook on secondary aggregates. The medium, which contains all relevant information of the Secondary Aggregate Directive, is made available to interested parties as printed copy and online. more




